在Shader编程中,插值算法是实现平滑过渡的关键技术。
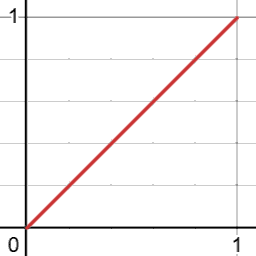
线性插值
线性插值 Lerp
Lerp 是最基本的插值,适用于颜色、位置、UV等标量或向量。
- 公式: $$ \text{lerp}(a, b, t) = a + t \cdot (b - a) $$ 或 $$ \text{lerp}(a, b, t) = a \cdot (1 - t) + b \cdot t $$
- 图示:
- 内置函数:
- HLSL:
lerp(a, b, t) - GLSL:
mix(a, b, t)
- HLSL:
球形线性插值 Slerp
Slerp 常用于在单位向量或四元数之间进行插值,特别是在动画和相机旋转中,它能够保持恒定的角速度,从而实现更自然的过渡效果。
- 公式: $$ \text{slerp}(v_0, v_1, t) = \frac{\sin((1 - t)\cdot\theta)}{\sin(\theta)} v_0 + \frac{\sin(t\cdot\theta)}{\sin(\theta)} v_1 \quad \text{其中 } \theta = \cos^{-1}(v_0 \cdot v_1) $$
- 简单实现:
vec3 slerp(vec3 v0, vec3 v1, float t) {
float theta = acos(dot(v0, v1));
return (sin((1.0 - t) * theta) * v0 + sin(t * theta) * v1) / sin(theta);
}- 实现注意事项:
- Slerp计算消耗较大,若插值角度较小,建议直接使用线性插值
lerp。 - 如果点积为负,则翻转其中一个向量,即确保选择最短路径进行插值。
- 避免除以零,当 θ 接近 0 时应退化为线性插值
lerp。
- Slerp计算消耗较大,若插值角度较小,建议直接使用线性插值
非线性插值
Smoothstep
Smoothstep 将值映射到范围[ edge0 , edge1 ],但以一种更平滑的方式,使得结果在接近边界时的变化更加缓慢,而在中间部分变化较快。
- 公式: $$ t’ = \text{saturate}(\frac{t - edge_0}{edge_1 - edge_0}) $$ $$ \text{smoothstep}(t’) = 3(t’)^2 - 2(t’)^3 \quad \text{其中 } t’ \in [0, 1] $$
-
- 内置函数:
- HLSL:
smoothstep(edge0, edge1, t) - GLSL:
smoothstep(edge0, edge1, t)
- HLSL:
- 内置函数:
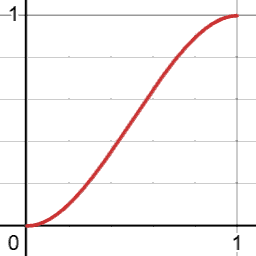
Smootherstep
Smootherstep 则是对 Smoothstep 的改进,提供了更加平滑的过渡效果。
- 公式: $$ t’ = \text{saturate}(\frac{t - edge_0}{edge_1 - edge_0}) $$ $$ \text{smootherstep}(t’) = 6(t’)^5 - 15(t’)^4 + 10(t’)^3 \quad \text{其中 } t’ \in [0, 1] $$
- 图示:
- 实现:
float Smootherstep(float edge0, float edge1, float t)
{
float t = saturate((x - edge0) / (edge1 - edge0));
return t * t * t * (t * (6.0f * t - 15.0f) + 10.0f);
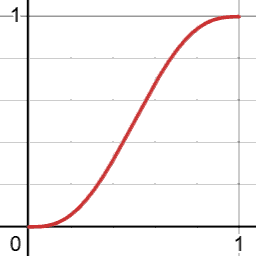
}正弦插值 Sine Interpolation
正弦插值通常指的是利用正弦函数的特性进行平滑过渡的一种插值技术。实际上并没有一个标准的“正弦插值”公式,通常是开发者自定义的。不常用
- 公式: $$ f(t) = \sin(\frac{\pi}{2} \cdot t) \quad\text{其中 } t \in [0, 1] $$
- 图示:
- 实现:
float f(float t) {
return sin((PI / 2.0f) * t);
}其中PI可能需要手动定义